Aquaculture, Fisheries and Fish Farming in India
India is the world’s third-largest producer of fish. The aquaculture sector accounts for around 69 per cent of the country’s total fish production. In addition, India is the world’s top producer and exporter of culture shrimp, with $ 5 billion in exports in FY 2019. The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairy, is executing the “Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY)- A programme to bring about a Blue Revolution.
As a result, aquaculture is one of the world’s fastest-growing industries. India’s extensive coastline region provides abundant fishing chances in both marine and interior waters. The country has the world’s second-largest aquaculture market share. Aquaculture has risen dramatically in recent years, becoming a significant economic sector. It is now the world’s fastest expanding food-producing sector, having the greatest potential to fulfil the rising demand for aquatic food. For anyone trying to start a business in this vast industry, it may appear impossible, but consultancy services such as KisaanMitrr provide fish farming consultancy services using a variety of methods such as cage system farming, pond fish farming, and composite fish culture, which make the task of starting a business not only simple but also profitable.
Probiotics in Aquaculture
Probiotics have been shown to aid in the growth, survival, and health of aquatic animals. In aquaculture, intestines, gills, aquatic animals’ skin mucous, environments, and even culture collections and commercial items can provide adequate probiotics, which have been recognised as bacteria and non-bacteria.
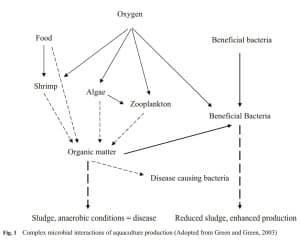
Because illnesses are causing enormous losses in aquaculture, there are a variety of ways that may be utilised to safeguard farmed aquatic animals against viruses. Probiotics are one of these treatments that have gained a lot of traction in the fight against illness. Probiotics were first defined as organisms and chemicals that contribute to gut microbial equilibrium.
Uses of Probiotics in Aquaculture
-
Improvement in water qualities
Contamination of fish culture ponds with nitrogenous substances such as ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate has been a major problem. Although the vulnerability of cultured aquatic species to high concentrations of these compounds varies by species, these chemicals can be exceedingly hazardous and cause mass mortality in all situations when present in high quantities. Lactobacillus spp. JK-8 and JK-11 have been shown to remove nitrogen and pathogens from polluted shrimp farms concurrently. Water quality has been enhanced by adding probiotics, particularly Bacillus spp., in multiple additional investigations.
-
As growth promoters
Experimentation has shown that probiotics can help fish develop faster. It was classified as a probiotic bacterium because it has the potential to outgrow pathogens in favour of the host or to boost the host’s growth while having no negative effects on the host.
-
For disease prevention
Probiotics or their products have been proven to be beneficial to the host in aquaculture, terrestrial animals, and human disease management. Microbial adjuncts that inhibit pathogens from growing in the intestine, on the surface of the skin, and in the culture environment of the culture species are among them. The beneficial organisms’ effect is achieved by enhancing the immune system of the culture organism, improving their disease resistance, or creating inhibitory substances that prevent harmful organisms from infecting the host.
-
Nutrient source and enzyme contribution to digestion
Microorganisms may have a favourable influence on the digestive processes of aquatic animals, according to some studies. Bacteroides and Clostridium sp. have been shown to contribute to the nutrition of fish hosts, particularly by delivering fatty acids and vitamins.
-
Improving the immune system’s responsiveness
One of the most widely claimed advantages of probiotics is that they help to modulate the immune system.
-
Aquaculture management using probiotics
The probiotic bacteria can be fed to the aquaculture managers, or they can be injected or immersed in the water.
Conclusions
Antibiotic overuse has resulted in a high number of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a concern to fish and humans who consume contaminated seafood. Inefficiencies in the treatment of fish infections with antibiotics result in large financial losses. However, the use of probiotics in aquaculture has been found to improve fish health and, as a result, the economic performance of fish farming. Using probiotics, on the other hand, provides significant environmental advantages. By reducing disease risk, the need for medication is reduced, and thus the risk of residues being left in the environment is reduced. If you are looking to get into the business of aquaculture and need help, look no further than the expert advice provided by KisaanMitrrs aquaculture consulting services. Get in touch today!

